一、前言
在这个春回大地万物复苏的日子,在家里带着口罩,手持消毒液.分析spring是最好消磨时间的方式.不知道在这段时间里面,能否把IOC这个分析完.
Resource 这个接口抽象了资源的获取方式, spring 启动往往都是从这一步开始.
二、从那几句代码开始
- 简单的java bean
package com.sjr.test.bean;
public class MyTestBean {
private String testStr = "test--one";
public String getTestStr() {
return testStr;
}
public MyTestBean setTestStr(String testStr) {
this.testStr = testStr;
return this;
}
}
- 一个xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN" "https://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans-2.0.dtd">
<beans>
<bean id="myTestBean" class="com.sjr.test.bean.MyTestBean"/>
</beans>
- 一段test 代码
package com.sjr.test;
import com.sjr.test.bean.MyTestBean;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
public class TestSpringBean {
@Test
public void testSpringLoadXml(){
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("com/sjr/test/bean/MyTestBean.xml"));
final MyTestBean testBean = factory.getBean("myTestBean",MyTestBean.class);
final String testStr = testBean.getTestStr();
System.out.println(testStr);
}
}
- 一个输出结果
test--one
可以看到spring从xml读取到了配置信息,并且符合预期的获取了bean.那么spring是如何加载xml的?在创建XmlBeanFactory的时候,构造方法接收的是一个Resource对象,Resource是个接口,这里直接使用的它的实现类ClassPathResource.
2.1 Resource 接口
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
/*
* 判断资源是否存在
**/
boolean exists();
/**
* 判断资源是否可读,默认方法JAVA8 新特性
*/
default boolean isReadable() {
return exists();
}
/**
* 判断文件是否被打开,默认方法JAVA8 新特性
* 默认返回 false
*/
default boolean isOpen() {
return false;
}
/**
* 判断资源是否是文件,默认方法JAVA8 新特性
* 默认返回 false
*/
default boolean isFile() {
return false;
}
/**
* 获取资源URL 对象
*/
URL getURL() throws IOException;
/**
* 获取资源 URI 对象
*/
URI getURI() throws IOException;
/**
* 获取资源文件对象
*/
File getFile() throws IOException;
/**
* 获取资源 Channel 对象 NIO
*/
default ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException {
return Channels.newChannel(getInputStream());
}
/**
* 获取资源长度
*/
long contentLength() throws IOException;
/**
* 获取资源最后修改时间
*/
long lastModified() throws IOException;
/**
* 创建资源相对路径
*/
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
/**
* 获取资源文件名
*/
@Nullable
String getFilename();
/**
* 获取资源描述信息
*/
String getDescription();
}
Resource 接口相当于对资源的一种抽象,不管是什么 xml 也好,字节流也好等,统一抽象,由不同的子类分别去实现.
2.2 XmlBeanFactory
- 回到问题本身,XmlBeanFactory是怎么加载xml的?
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory {
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
this(resource, null);
}
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
// 从这里开始,加载xml
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); // A
}
}
从A 处XmlBeanFactory,委托XmlBeanDefinitionReader进行加载xml.跟踪进去看看.
2.3 XmlBeanDefinitionReader
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 把classPathsResource转换为EncodedResource,默认字符编码为空
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 加载资源,资源不能为空
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
// 判断当前线程是否加载过资源,如果没有则创建一个set来保存encodedResource
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
// 判断是否有已近添加过相同的encodedResource
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
// 获取xml文件流
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
// 如果编码不为空,则设置文件编码
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
// 加载bean
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
从XmlBeanDefinitionReader代码逻辑可以看出:
- 把
Resource对象转换为EncodedResource对象 - 判断 xml 资源是否被加载过,如果被加载过 抛出异常
BeanDefinitionStoreException - xml 资源放入缓存
- 获取资源流
- 读取文件
- 关闭文件流
emmm,那么EncodedResource 对象是个什么玩意儿呢?? 跟踪进去看看.
2.4 EncodedResource
public class EncodedResource implements InputStreamSource {
// 资源对象
private final Resource resource;
// 编码
@Nullable
private final String encoding;
// 字符集
@Nullable
private final Charset charset;
public EncodedResource(Resource resource) {
this(resource, null, null);
}
public EncodedResource(Resource resource, @Nullable String encoding) {
this(resource, encoding, null);
}
public EncodedResource(Resource resource, @Nullable Charset charset) {
this(resource, null, charset);
}
private EncodedResource(Resource resource, @Nullable String encoding, @Nullable Charset charset) {
super();
Assert.notNull(resource, "Resource must not be null");
this.resource = resource;
this.encoding = encoding;
this.charset = charset;
}
/**
* 返回资源对象
*/
public final Resource getResource() {
return this.resource;
}
/**
* 获取编码
*/
@Nullable
public final String getEncoding() {
return this.encoding;
}
/**
* 获取字符集
*/
@Nullable
public final Charset getCharset() {
return this.charset;
}
/**
* 如果编码 和 字符集 不为空
* 则需要reader对象
*/
public boolean requiresReader() {
return (this.encoding != null || this.charset != null);
}
/**
* 获取 Reader 对象
*/
public Reader getReader() throws IOException {
if (this.charset != null) {
return new InputStreamReader(this.resource.getInputStream(), this.charset);
}
else if (this.encoding != null) {
return new InputStreamReader(this.resource.getInputStream(), this.encoding);
}
else {
return new InputStreamReader(this.resource.getInputStream());
}
}
/**
* 获取流对象
*/
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return this.resource.getInputStream();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) {
if (this == other) {
return true;
}
if (!(other instanceof EncodedResource)) {
return false;
}
EncodedResource otherResource = (EncodedResource) other;
return (this.resource.equals(otherResource.resource) &&
ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.charset, otherResource.charset) &&
ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.encoding, otherResource.encoding));
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.resource.hashCode();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.resource.toString();
}
}
EncodedResource内部的逻辑很简单,并未做什么特殊操作,看来EncodedResource只是加了几个工具方法而已,比如获取Reader.
那么接下的重点就是,如何获取xml文件的.上面代码中的Resource对象的实现类是ClassPathResource,获取文件流的代码如下.
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
InputStream is;
// 如果指定的 class 对象不为空
if (this.clazz != null) {
// 获取流对象
is = this.clazz.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
// 如果指定的 classLoader 对象不为空
else if (this.classLoader != null) {
// 获取流对象
is = this.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
else {
// 获取流对象
is = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
// 流对象为空 抛出异常 FileNotFoundException
if (is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be opened because it does not exist");
}
return is;
}
三、Resource 体系
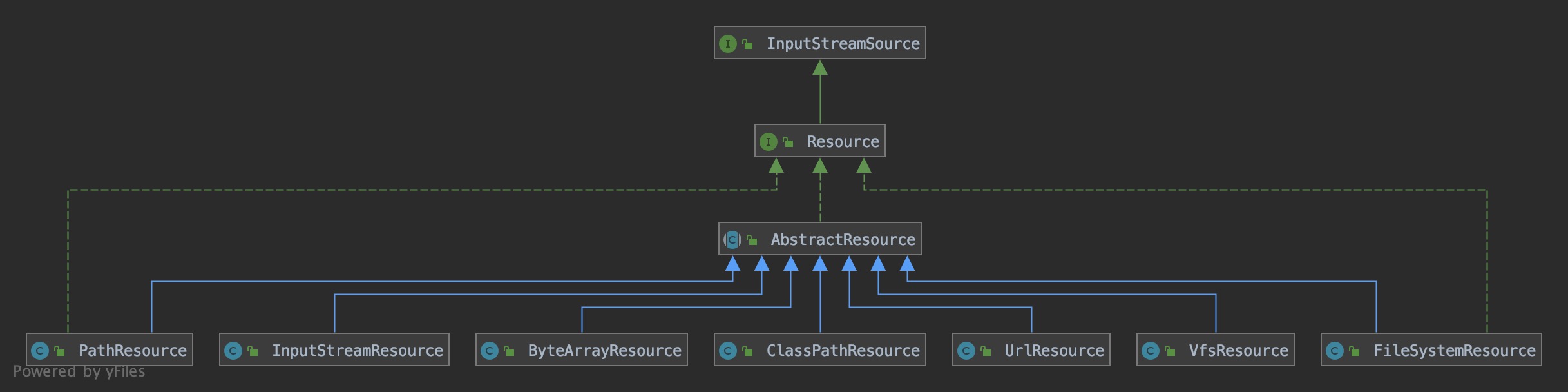
-
FileSystemResource
对
java.io.File类型资源的封装,只要是跟 File 打交道的,基本上与 FileSystemResource 也可以打交道。 -
ByteArrayResource
对字节数组提供的数据的封装。如果通过 InputStream 形式访问该类型的资源,该实现会根据字节数组的数据构造一个相应的 ByteArrayInputStream。
-
UrlResource
对
java.net.URL类型资源的封装。内部委派 URL 进行具体的资源操作。 -
ClassPathResource
class path 类型资源的实现。使用给定的 ClassLoader 或者给定的 Class 来加载资源。
-
InputStreamResource
将给定的 InputStream 作为一种资源的 Resource 的实现类。
-
VfsResource
VfsResource代表Jboss 虚拟文件系统资源。
以上6种常用的 Resource 对象,当然spring 里面可不止这6中 Resource 实现类.
四、思考
在 spring 配置文件中,有些资源可能不是从 classPath 获取,可能是从网络获取等,那么 spring 是怎么知道要用那种方式进行资源加载的呢?
也许跟 ResourceLoader 这个有关.